Institutional storage of Bitcoin involves sophisticated, multi-layered security architectures that combine hardware, cryptography, and regulatory frameworks to protect digital assets at scale. Understanding how exchanges, ETFs, and custodians safeguard Bitcoin requires examining the technical mechanisms, custody models, and operational practices that define institutional-grade security.
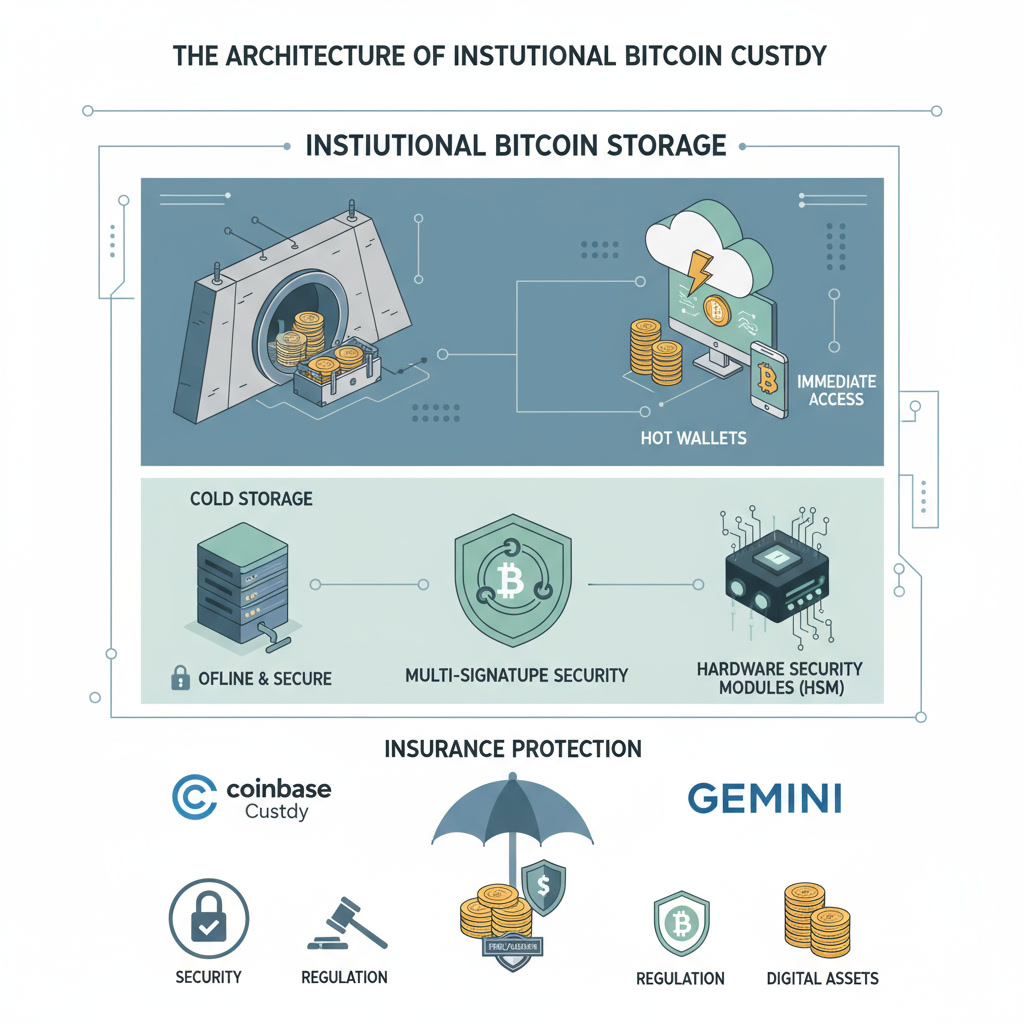
Storage Architecture: Hot and Cold Wallets
Institutions employ a dual-wallet strategy to balance security with operational efficiency. Cold storage maintains the majority of Bitcoin holdings offline in hardware security modules (HSMs) and air-gapped systems that are never connected to the internet. This approach eliminates online attack vectors and significantly reduces hacking risks, making it suitable for long-term holdings and large asset amounts.
Conversely, hot wallets store a smaller portion of Bitcoin online for immediate liquidity to facilitate trading, withdrawals, and daily operational needs. Most custodians maintain a typical allocation of 2% of assets in hot storage and 98% in cold storage. This hybrid approach enables custodians to fulfill client requests without exposing the entire asset base to internet-connected risks while maintaining institutional-grade security standards.
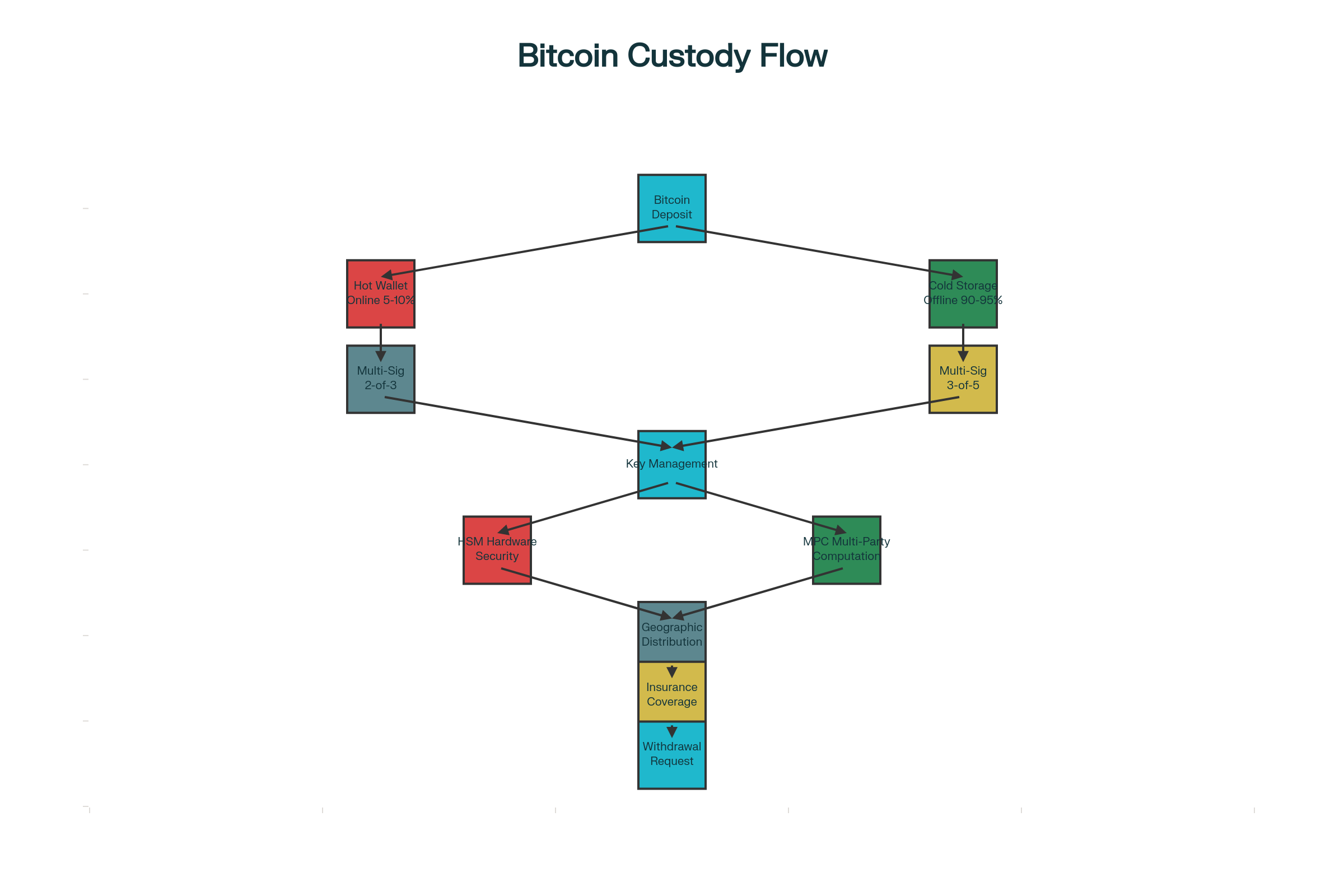
Key Management Technologies
Modern institutional custody relies on three primary key management technologies: Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig) arrangements, and Multi-Party Computation (MPC).
Hardware Security Modules are specialized physical devices that generate, store, and isolate private keys within tamper-resistant hardware certified to FIPS 140-2 standards. These devices never expose keys externally and automatically erase stored keys if physical tampering is detected. HSMs form the foundation of cold storage for custodians like Gemini, whose hardware security modules are housed in geographically distributed secured facilities that require proper credentials to access. BitGo and other major custodians integrate HSMs into their infrastructure to ensure private keys remain isolated during cryptographic operations.
Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig) technology requires multiple independent private keys—typically arranged as “m-of-n” configurations—to authorize Bitcoin transactions. A common arrangement is 2-of-3, where any two of three keys can authorize a transaction, preventing a single compromised key from enabling theft. This distributed approach eliminates single points of failure and is particularly effective for large institutional holdings. For example, Bitfinex’s cold storage wallet uses a 3-of-6 multisig arrangement.
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) takes key management further by distributing private key components across multiple parties and locations, ensuring no single entity ever possesses the complete key. This technology is increasingly adopted by next-generation custodians and creates redundancy without needing physical hardware. BitGo’s custody infrastructure pairs three-key multi-signature cold storage with MPC-TSS (Threshold Signature Scheme), eliminating any single point of failure by ensuring the private key is never reconstructed or exposed.
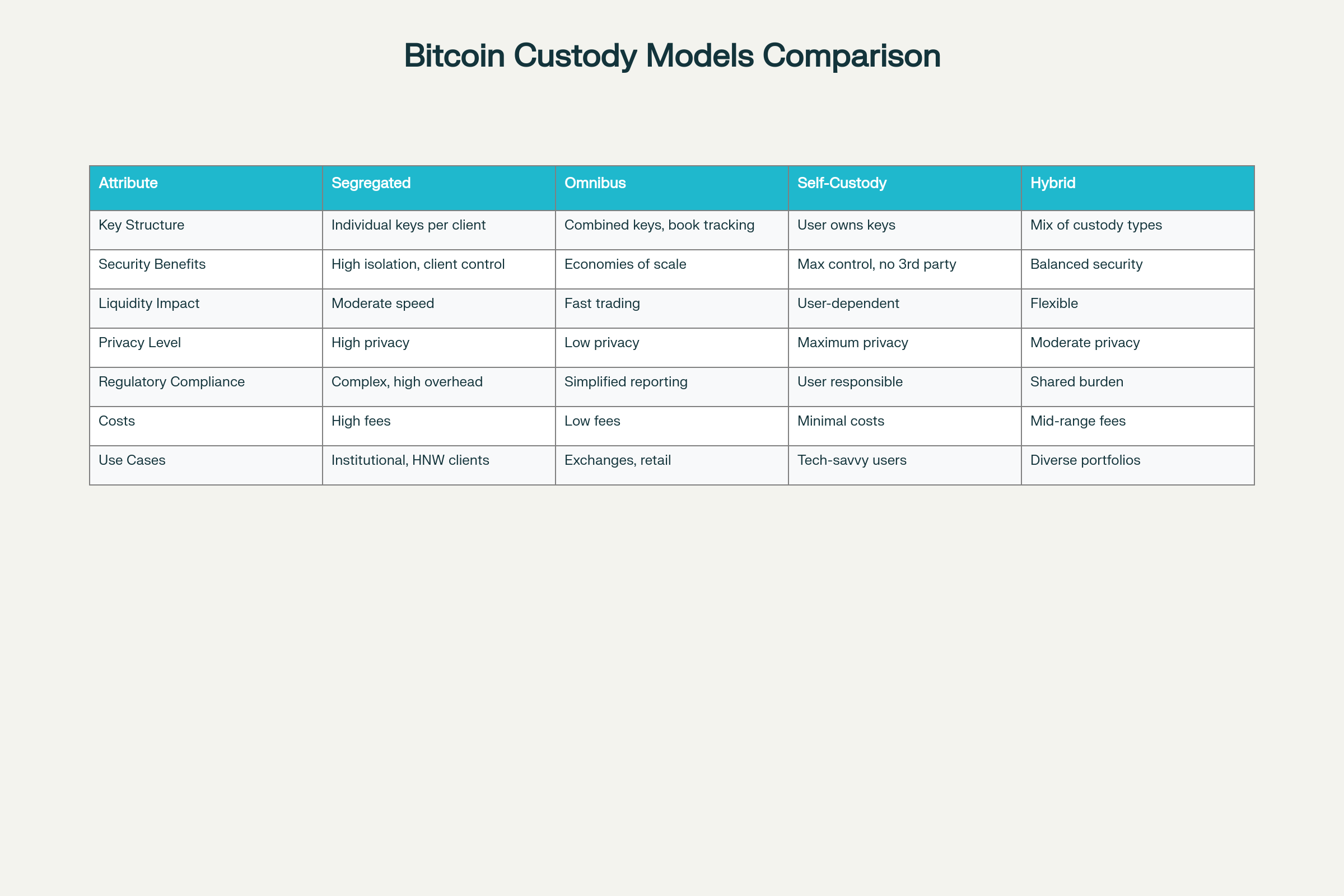
Custody Models: Segregated vs. Omnibus
Custodians implement one of two primary models for organizing client assets: segregated custody and omnibus custody, each with distinct security and operational characteristics.
Segregated custody maintains separate private and public key pairs for each client on-chain. This approach provides maximum transparency because assets are verifiable directly on the blockchain without relying on custodian records. Each ETF sponsor using segregated custody can independently verify their Bitcoin holdings through blockchain explorers. However, segregated custody introduces liquidity challenges: when multiple clients request withdrawals simultaneously, the custodian must perform separate fund transfers from cold storage for each client, requiring complex coordination and multiple transactions that increase operational costs and processing time.
Omnibus custody combines client assets across multiple key pairs but maintains segregation at the books-and-records level within the custodian’s accounting systems, similar to how the Depository Trust Company (DTC) handles traditional securities. This model uses Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) protocols to generate master private keys that produce near-infinite child keys, enabling flexible asset distribution across multiple storage environments without requiring separate keys per client.
The omnibus approach offers superior liquidity management: a custodian with omnibus structure and $20,000 in hot storage can fulfill three simultaneous $5,000 withdrawal requests without moving assets from cold storage, whereas segregated custody would require complex cold storage rebalancing for each withdrawal. Omnibus custody also provides enhanced privacy since addresses cannot be linked to individual clients. However, clients must rely on custodian records and audits to verify holdings rather than blockchain transparency.
Bitcoin Movement: Deposits and Withdrawals
The process of holding Bitcoin at institutional custodians involves formal onboarding and custody transfer procedures. When an ETF sponsor like BlackRock or Ark receives new fund inflows, Authorized Participants trigger the creation of new ETF shares, which the sponsor then directs the custodian to purchase Bitcoin on its behalf.
The custodian executes a private key generation ceremony—a highly orchestrated process involving multiple stakeholders, internal auditors, and potentially independent external auditors witnessing the creation of master key pairs that will secure client funds. This ceremony ensures the private key generation follows secure, tamper-proof, rules-based processes. For Coinbase Custody, this includes offline creation of public/private key pairs with a designated employee serving as scribe documenting every ceremony step.
For withdrawals, custodians employ multi-party and multi-stage cold restore protocols to authorize transactions. BitGo’s withdrawal process requires multiple independent key signatures from its secure network, supplemented by video identity verification, liveness detection for real-time biometric checks, and customizable policy controls that clients configure based on their risk tolerance.
Regulatory Framework and Custodian Qualification
Institutional Bitcoin custodians must meet rigorous regulatory standards established primarily through New York Banking Law. Leading custodians including Coinbase Custody, Gemini Custody, and others operate as Limited Purpose Trust Companies chartered by the New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS). This charter designates them as fiduciaries held to the same compliance, security, and capital requirements as traditional financial custodians.
Custodians must comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements and adhere to strict standards regarding capitalization, confidentiality, and storage protocols. Fidelity Digital Assets, which operates as its own custodian for Bitcoin ETFs, maintains fiduciary status through its established financial services infrastructure.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance protection is a critical component of institutional Bitcoin custody. Major custodians carry Lloyd’s of London-backed insurance policies that protect against losses from theft, hacking, and operational failures. BitGo maintains $250 million in insurance coverage provided by Lloyd’s, explicitly protecting against theft and operational failures. Gemini Custody secured $100 million in cold storage insurance coverage for certain cryptocurrency losses.
Lloyd’s marketplace syndicates now offer dynamic insurance policies where coverage limits adjust automatically based on Bitcoin price changes, ensuring clients remain indemnified for the underlying asset value even as market prices fluctuate. These policies typically cover institutional custodians, exchanges, and mining operations with limits reaching up to $200 million per entity.
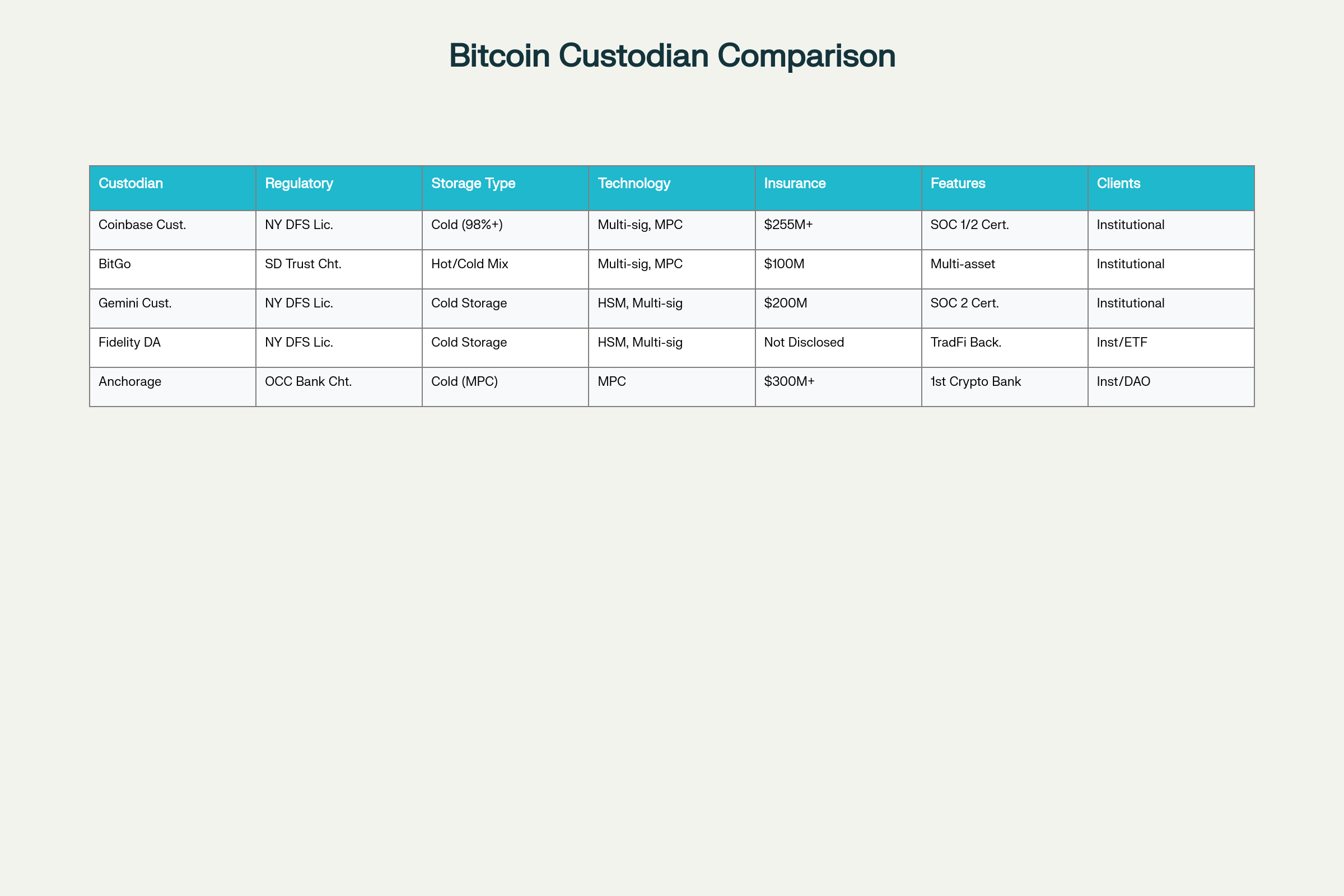
Major Custodians and Their Approaches
Coinbase Custody operates as a Limited Purpose Trust Company and custody provider for multiple Bitcoin ETFs including Ark’s Bitcoin ETF. The platform uses geographically distributed cold storage vaults with multi-layer encryption and offline private key storage to minimize hacking risks. Coinbase maintains segregated accounts where Bitcoin is held in separate wallets and not commingled with other customers’ assets.
BitGo, established as an early pioneer in multi-signature technology, employs a layered security model combining cold storage by default, multi-signature architecture with hardware-isolated keys, and MPC-TSS technology eliminating single points of failure. BitGo processes over 9.9 million wallets, supports over 1,100 digital assets, and has facilitated $2 trillion in lifetime transactions.
Gemini Custody uses hardware security modules storing private keys that never connect to the internet, achieving the highest levels of U.S. government security ratings. The platform implements multi-party technology, role-based governance protocols, physical security, and multiple layers of biometric access controls. Gemini Instant Trade enables institutional clients to trade directly with assets held in offline storage while maintaining high security standards.
Fidelity Digital Assets, operating through Fidelity’s established institutional infrastructure, holds a majority of Bitcoin in offline cold storage while maintaining operational flexibility for trading and withdrawals. Fidelity doesn’t publicly disclose the cold vs. hot storage allocation ratio, reserving complete discretion over these determinations.
Anchorage Digital provides institutional-grade custody using multi-factor authentication, cold storage, insured services, and 24/7 monitoring to prevent theft or loss. The platform integrates trading capabilities with custody infrastructure and provides automated compliance reporting.
Security Practices and Operational Standards
All institutional custodians implement multi-layered operational controls beyond cryptography. These include two-factor authentication for account access, withdrawal whitelisting systems that pre-approve trusted addresses, real-time monitoring for anomalous activity, biometric verification at critical operational stages, and travel rule compliance for transmitting transaction details between financial institutions.
Custodians conduct regular third-party security audits and SOC 1 Type 2 and SOC 2 Type 2 certifications to validate their security controls and operational integrity. These audits provide independent verification that custody arrangements align with industry best practices regarding key generation, storage, backup, and disaster recovery.
ETF-Specific Custody Considerations
Bitcoin ETFs introduce specific custody requirements because the underlying Bitcoin must remain secured and segregated from ETF sponsor assets and the custodian’s own holdings. Most Bitcoin spot ETFs rely on a single dedicated custodian—Coinbase Custody serves eight ETFs while Gemini serves VanEck’s offering. ETF documentation typically specifies that Bitcoin is held in cold storage “unless required to facilitate withdrawals as a temporary measure,” establishing that cold storage is the default position.
The ETF sponsor maintains ultimate responsibility for selecting and potentially replacing custodians, providing an additional governance layer of protection for investors. BlackRock’s Bitcoin ETF documents explicitly state that the sponsor may independently add or terminate Bitcoin custodians based on its discretion.
Addressing Custodial Risks
Despite robust security infrastructure, institutional custody maintains certain inherent risks. Counterparty risk remains the primary concern—if a custodian faces regulatory intervention, insolvency, or significant security breach, even well-insured holdings may face temporary inaccessibility or complications. This risk is why some institutional investors maintain hybrid custody arrangements, storing portions in self-custody while holding other amounts with qualified custodians.
Operational risk emerges from human error, key management failures, or compromised insiders. The $100 million Lloyd’s insurance facility secured by Onramp Bitcoin specifically addresses “internal threats such as collusion,” providing coverage against human risk vectors within custody frameworks.
Regulatory risk varies by jurisdiction; custodians operating as trust companies under New York Banking Law face different requirements than those regulated in EU jurisdictions under MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation), creating potential gaps in cross-border custody arrangements.
The Trade-off Between Control and Security
Institutional custody inherently involves trading direct control for professional-grade security and regulatory compliance. Users who hold Bitcoin through custodians lose access to direct blockchain interaction—they cannot participate in DeFi protocols, earn staking rewards, or execute peer-to-peer transactions that self-custody enables. Conversely, users maintain reduced personal responsibility for key management, eliminating the catastrophic risk of permanently losing Bitcoin through misplaced private keys or recovery phrases.
The choice between institutional custody and self-custody ultimately reflects risk preferences: institutional custody prioritizes security through professional infrastructure and insurance, while self-custody prioritizes autonomy and eliminates third-party dependencies at the cost of greater personal security responsibility.
Ready to start your cryptocurrency journey?
If you’re interested in exploring the world of crypto trading, here are some trusted platforms where you can create an account:
- Binance – The world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange by volume.
- Bybit – A top choice for derivatives trading with an intuitive interface.
- OKX – A comprehensive platform featuring spot, futures, DeFi, and a powerful Web3 wallet.
- KuCoin – Known for its vast selection of altcoins and user-friendly mobile app.
These platforms offer innovative features and a secure environment for trading and learning about cryptocurrencies. Join today and start exploring the opportunities in this exciting space!

Join our crypto community for news, discussions, and market updates: CryptoBCC on Youtube | Instagram | Telegram | Pinterest | Facebook | Discord | Tiktok | Threads | X(Twitter).

Disclaimer: This is not investment advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry high risk. Always conduct your own research.